Why do I have tooth sensitivity?
Knowing a bit more about the structure of your teeth will help you understand the reasons for tooth sensitivity.
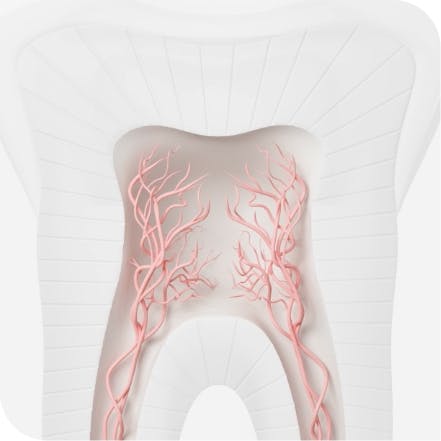
The outer layer of your teeth is called enamel, and is the strongest part. Underneath the enamel is a soft layer called dentine. The short, sharp twinge of pain you get with tooth sensitivity is caused when the enamel is weakened and the soft dentine inside your tooth becomes exposed, revealing the tiny pores inside it. These pores are the openings to channels that run through your dentine straight to the centre of the tooth where the nerve is. When you eat or drink something cold, hot, sweet or sour, this stimulus can travel through the pores and irritate the nerve, and this is what causes tooth sensitivity pain.1
What are the reasons for tooth sensitivity?
There are many reasons why you may have tooth sensitivity including:
- Receding gums caused by gum disease.
- Over-enthusiastic brushing, or brushing with a toothbrush that’s too hard.
- Eating and drinking too many acidic foods and drinks.
- Grinding your teeth.
- Tooth decay, or injury to your teeth.
- A recent dental procedure.2
Who’s most likely to be vulnerable to tooth sensitivity?
Anyone can suffer from tooth sensitivity, but it’s more common in people between the ages of 20 and 40, and women are more likely to experience tooth sensitivity than men.3
How should I manage my tooth sensitivity?
One of the ways you can address tooth sensitivity is by using a fluoride toothpaste for sensitive teeth to brush your teeth twice a day.
Other ways of helping prevent what causes tooth sensitivity include:
- Brushing your teeth twice a day, in the morning and just before you go to bed, using a toothpaste for sensitive teeth that contains at least 1,350 parts per million (ppm) of fluoride. Use small, circular motions with a soft toothbrush. The NHS recommends brushing your teeth for two minutes each time.
- Change your toothbrush every three months.
- After eating, wait a while before brushing your teeth.
- Try to avoid sugary foods, and fizzy or acidic drinks.
- If you grind your teeth, ask your dentist about having a custom-made mouth guard.
- Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups.4
What causes tooth pain?
Tooth pain causes include:
- Tooth decay.
- Dental abscesses.
- Cracked or damaged teeth, or a loose or broken filling.
- An infection, which often happens when a new tooth (like a wisdom tooth) is emerging, but it hasn’t broken through the skin yet.
Visit your dentist if you experience ongoing discomfort, so that they can identify the cause of tooth pain for you, and treat it.5
How can I help prevent some of the causes of tooth pain?
Brush your teeth with a fluoride toothpaste twice a day to stop plaque building up, which can lead to tooth decay. If you’re an adult, your toothpaste should include at least 1,350ppm of fluoride. Children can use the same toothpaste as adults, although children under three years should just use a small smear.
Sources: Clicking any of the links below takes you to an external website that is independently operated and not managed by GSK. GSK assumes no responsibility for the content on the website. If you do not wish to leave this website, do not click on the links below.